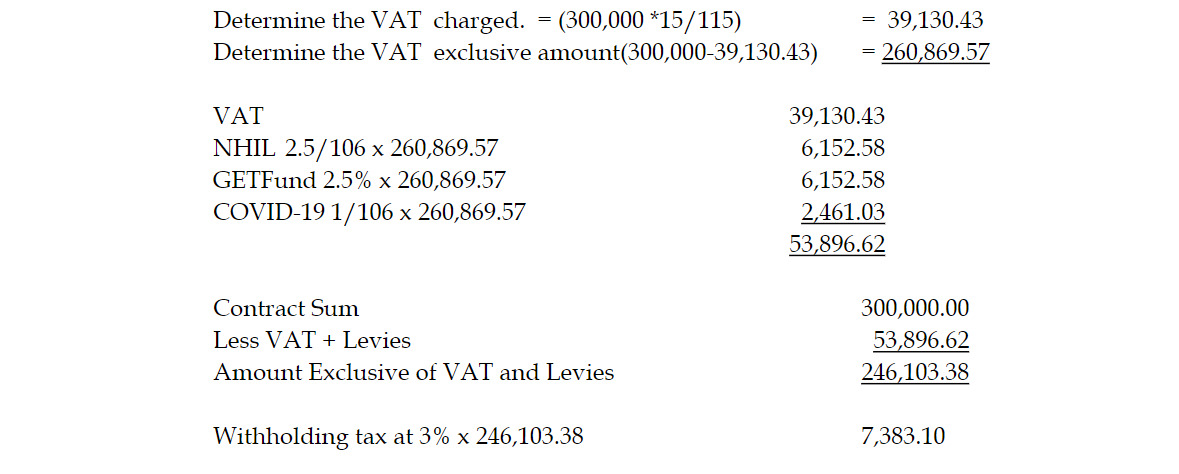
- 10 Marks
Question
Although the scope of withholding tax covers employment, business, and investment income, not every income is subject to withholding tax in accordance with the Income Tax Act, 2015 (Act 896) as amended.
Required:
Explain FOUR (4) of these withholding tax exemptions.
(10 marks)
Answer
The following payments are exempted from withholding tax:
- Premium paid to a resident insurance company.
- Payment for the sale of goods which constitute trading stock of both the vendor and the purchaser.
- Interest or dividend paid or credited to a holder or member on the investment in an approved unit trust scheme or mutual fund.
- Interest paid to a resident financial institution.
- Payments made to persons specifically exempted from tax.
- Income or activity exempted from tax.
- Payments that have been granted exemption from withholding tax by the Commissioner-General.
- Dividend paid by a resident company to another resident company that controls directly or indirectly at least 25% of the voting power in the company paying the dividend. This does not include redeemable shares.
- Cumulative contract sums of the supply of goods, services, and works not exceeding GH¢ 2,000.
(Any 4 points @ 2.5 marks each = 10 marks)
- Topic: Exemptions, Withholding Tax Administration
- Series: APR 2022
- Uploader: Cheoli