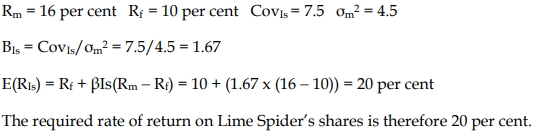- 4 Marks
Question
c) Ten years ago, Brown Limited issued GH¢2.5 million of 6% discounted debentures at GH¢98 per 100 nominal. The debentures are redeemable in 5 years from now at GH¢2 premium over nominal value. They are currently quoted at GH¢80 per debenture ex-interest. Brown Limited pays corporate tax at the rate of 30%.
You are required to calculate the cost of debt after tax.
(4 marks)
Answer
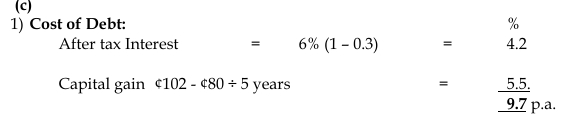

- Tags: Capital structure, Cost of Debt, Debentures, Taxation
- Level: Level 3
- Uploader: Dotse