- 10 Marks
Question
Asanka Ghana Ltd is a medium-sized business in Ghana that is currently borrowing GH¢1,000,000 from North East Bank at a floating or variable interest rate basis at Ghana Reference Rate (GRR) plus 3% margin which is market determined on a monthly basis. This makes their monthly interest payment volatile depending on where GRR is at the end of the month. They are rather interested in fixed interest payment at the end of the month to manage this volatility.
OTI Bank Ghana Ltd has agreed to do an Interest rate Swap with Asanka where OTI Bank Ghana Ltd pays the variable rate to Asanka but Asanka pays them a fixed rate of 21% per annum paid monthly.
The table below shows the GRR for the last 6 months:
| Month | GRR (%) | Variable Interest (C) | Fixed Rate (D) | Fixed Interest (E) | Net Settlement (F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16% | 21% | |||
| 2 | 18% | 21% | |||
| 3 | 20% | 21% | |||
| 4 | 19% | 21% | |||
| 5 | 18% | 21% | |||
| 6 | 17% | 21% |
Required:
i) Calculate the variable interest, fixed interest, and net settlement under columns (C), (E), and (F) in the table above.
(8 marks)
ii) Will you describe this strategy as an interest rate hedge? Explain.
(2 marks)
Answer
i) Calculation of Variable Interest, Fixed Interest, and Net Settlement:
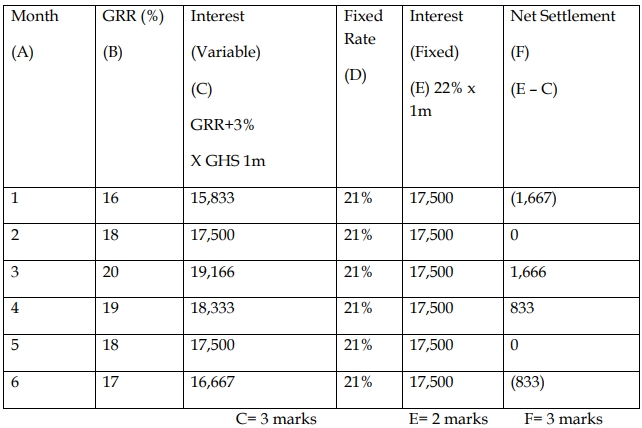
ii) Interest Rate Hedge Explanation:
Yes, this strategy can be described as an interest rate hedge. The variable rate that Asanka will receive under the swap agreement compensates for the variable rate it has to pay to its original lender, North East Bank. This effectively leaves Asanka with a fixed interest payment of 21%, thereby removing the uncertainty and volatility in its monthly interest payments.
(2 marks)
- Tags: Financial risk management, Hedging, Interest rate hedge, Interest rate swaps, Swaps
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Hedging with options
- Series: MAY 2020
- Uploader: Theophilus
