- 20 Marks
Question
Lolonyo Foam Ltd (Lolonyo), an Accra-based unlisted company, has been manufacturing mattresses and other foam products since 1990. The company is considering a new project which requires a GHS75 million investment in capital expenditure and net working capital. The directors of Lolonyo have decided to raise the needed funds through a new issue of 10-year subordinated bonds to investors in Ghana. Lolonyo uses a discount rate of 20% to appraise new projects. However, the directors feel that this rate will not be appropriate for this project as its financing method is different from what has been used in the past.
The following information is available for the company:
Total assets: GHS150m
Long-term debt: GHS80m
Net income: GHS10.2m
Net income before interest and taxes: GHS14.8m
Interest payments: GHS1.2m
Tax rate: 25%
Earnings of the company for the past five years are as follows:
| Year | Earnings (GHS’m) |
|---|---|
| 2014 | 9.8 |
| 2013 | 9.2 |
| 2012 | 8.5 |
| 2011 | 8.1 |
| 2010 | 8.4 |
Directors intend to use the Kaplan Urwitz model for unlisted companies to assess the cost of debt. The Kaplan Urwitz model for unlisted companies is given by:
Y=4.41+0.001(Size)+6.40(Profitability)−2.56(Debt)−2.72(Leverage)+0.006(Interest)−0.53(COV)
Where:
- Y is the credit score
- Size is measured by total assets
- Profitability is measured by the ratio of net income to total assets
- Debt refers to the status of the debt stock; subordinated debt is assigned score 1, and unsubordinated debt is assigned score 0
- Leverage is measured by the ratio of long-term debt to total assets
- Interest refers to interest cover, which is measured by net operating income (i.e. net income before interest and tax)
- COV is the coefficient of variation in earnings, which measures volatility in earnings
The table below presents credit score ranges and corresponding rating categories and yields to maturity for 10-year corporate bonds:
| Score (Y) | Rating Category | Yield to Maturity |
|---|---|---|
| Y > 6.76 | AAA | 22.0% |
| Y > 5.19 | AA | 22.5% |
| Y > 3.28 | A | 23.2% |
| Y > 1.57 | BBB | 24.2% |
| Y > 0 | BB | 25.5% |
Required:
(a) Estimate the cost of debt. (8 marks)
(b) Suppose Lolonyo applies to a credit rating agency for rating of its debt. Explain any THREE (3) of the criteria the credit rating agency would use in establishing the company’s credit rating. For each criterion, suggest one factor that can be used to assess it. (6 marks)
(c) Suppose the fair market value of assets is GHS200 million and the face value of the 10-year bonds is GHS80 million. The risk-free rate is 18% and the volatility of asset value is 50%.
(i) Find the value of the default probability using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. (3 marks)
(ii) Estimate the expected loss on the bonds if the recovery rate is 60%. (3 marks)
(Total = 20 marks)
Answer
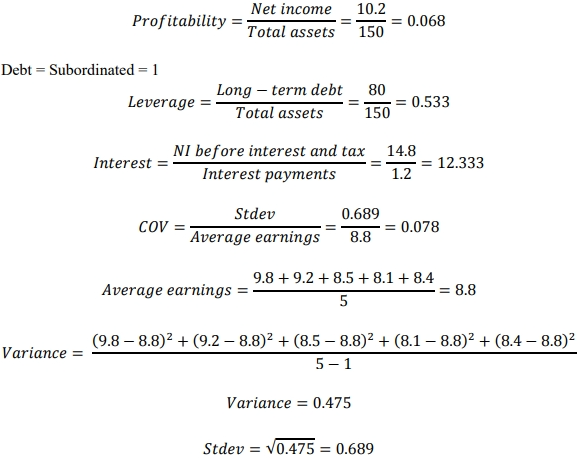
Calculate credit score (Y) using Kaplan Urwitz model for unlisted companies
𝑌 = 4.41 + 0.001𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒 + 6.40𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑓𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑖𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑦 − 2.56𝐷𝑒𝑏𝑡 − 2.72𝐿𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒
+ 0.006𝐼𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑡 − 0.53𝐶𝑂V
Where
Size is measured by total assets
Profitability is measured by the ratio of net income to total assets
Debt refers to the status of the debt stock; subordinated debt is assigned score 1, and
unsubordinated debt is assigned score 0
Leverage is measured by the ratio of long-term debt to total assets
Interest refers to interest cover, which is measured by net operating income (i.e. net
income before interest and tax)
COV is the coefficient of variation in earnings, which measures volatility in earnings
𝑆𝑖𝑧𝑒 = 𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑡𝑠 = 200
Note: Since company has been operating since 1990, earnings record for the past five
years is a sample of earnings. The standard deviation is therefore estimated as a sample
standard deviation.
𝑌 = 4.41 + 0.001(150) + 6.40(0.068) − 2.56(1) − 2.72(0.533) + 0.006(12.333)− 0.53(0.078)
𝑌 = 1.018
With a credit score of 1.018, Lolonyo falls into the BB credit rating.
The yield on 10-year corporate bonds with BB rating is 25.5%.
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑑𝑒𝑏𝑡 = 𝑌𝑇𝑀 × (1 – 𝑡𝑎𝑥 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒)
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑜𝑓 𝑑𝑒𝑏𝑡 = 25.5% × (1 – 0.25) = 19.125%
(b) Criteria used for credit rating
Criteria normally used by credit rating agencies in establishing credit rating of companies
include the following:
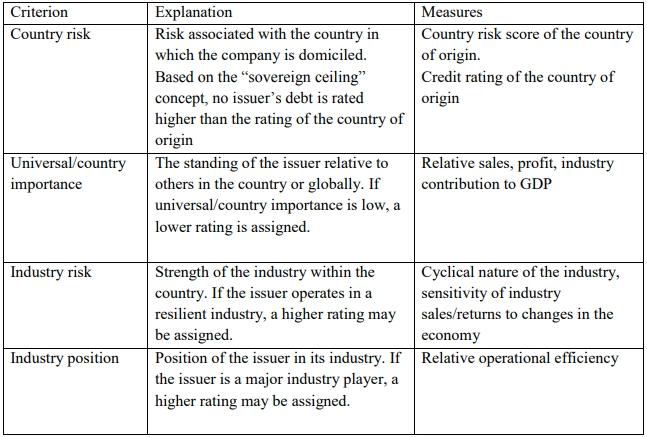
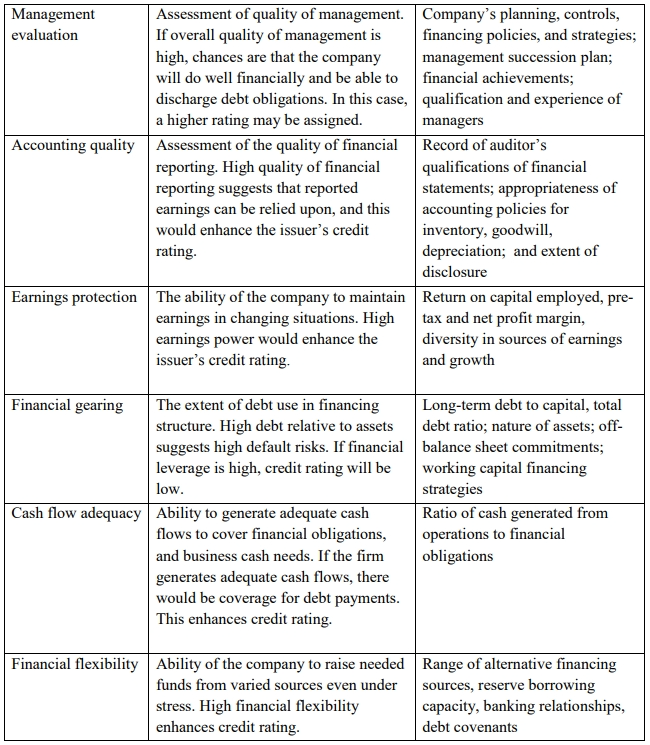
(c) Default Probability and Expected Loss:
(i) Default Probability:
Default probability is calculated using the Black-Scholes model:
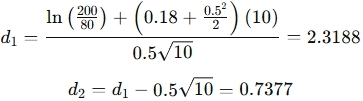
Using the cumulative normal distribution, N(d2) = 0.7704.
Default probability = 1 – N(d2) = 0.2296 or 22.96%.
(ii) Expected Loss:
Expected loss is calculated as:
Loss given default = GHS80m x (1 – 0.60) = GHS32m.
Expected loss = GHS32m x 0.2296 = GHS7.3472m.
- Tags: Cost of Debt, Credit Rating, Default Risk, Expected Loss, Kaplan Urwitz Model
- Level: Level 3
- Topic: Sources of finance and cost of capital
- Series: NOV 2015
- Uploader: Joseph
