- 20 Marks
Question
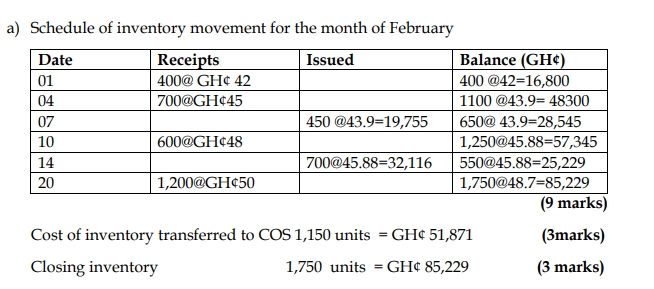
Question: a) The following extracts are from the books of Bediako Enterprise in the month of February:
| Date | Description | Units | Per unit cost (GH¢) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Receipts | 400 | 42 |
| 04 | Receipts | 700 | 45 |
| 07 | Issue | 450 | |
| 10 | Receipts | 600 | 48 |
| 14 | Issue | 700 | |
| 20 | Receipts | 1,200 | 50 |
Required: Using the Weighted Average Method;
i) Calculate the cost of goods issued to Cost of Sales. (3 marks)
ii) Compute the value of closing inventory. (12 marks)
b) Identify TWO (2) possible causes for each of the following variances:
i) Material cost variance.
ii) Labour cost variance. (5 marks)
Answer
b)
i) Possible Causes of the Materials Price Variance
If the standard price is reasonable, then a materials price variance may be caused
by such valid factors as the following:
Rush deliveries
Market-driven pricing changes, such as changes in the prices of commodities
Bargaining power changes by suppliers, who may be able to impose higher
prices than expected
Buying in unusually large or small volumes in comparison to what was expected
when the standard was created
A change in the quality of the materials purchased
ii) The possible causes of labor rate variance are:
Payment at a higher or lower rate than the standard
Changes in employee skills
Recruitment of new personnel
Changes in compensation methods, etc.
(Any 2 points for each variance @ 1.25 mark each = 5 marks)
- Topic: Inventory Management
- Series: AUG 2022
- Uploader: Joseph
