- 14 Marks
Question
a) The Directors of Mama Ltd (Mama), a large listed company, are considering an opportunity to
acquire all the shares of Papa Ltd (Papa), a small listed company with a highly efficient
production technology.
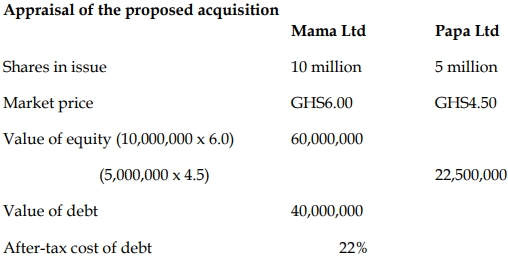
Mama has 10 million shares of common stock in issue that are currently trading at GH¢6.00
each. Papa Ltd has 5 million shares of common stock in issue, each of which is trading at
GH¢4.50.
If Papa is acquired and integrated into the business of Mama, the production efficiency of the
combined entity would increase and save the combined business GH¢600,000 in operating
costs each year to perpetuity.
Though Mama operates in the same industry as Papa, its financial leverage is higher than that
of Papa. Mama’s total debt stock is valued at GH¢40 million, and its after-tax cost of debt is
22%. The beta of Mama’s common stock is 1.2. The return on the risk-free asset is 20% and
the market risk premium is 5%.
Required:
Suppose Mama offers a cash consideration of GH¢25 million from its existing funds to the
shareholders of Papa for all of their shares.
i) Calculate the NPV of the acquisition, and advise the directors of Mama on whether to
proceed with the acquisition or not. (8 marks)
ii) Calculate the value of the combined entity immediately after the acquisition. (3 marks)
iii) Suppose Mama would like to acquire all the shares in Papa by offering fresh shares of its
own common stock to the shareholders of Papa. Advise the directors on the appropriate
share exchange ratio based on market price.
Answer
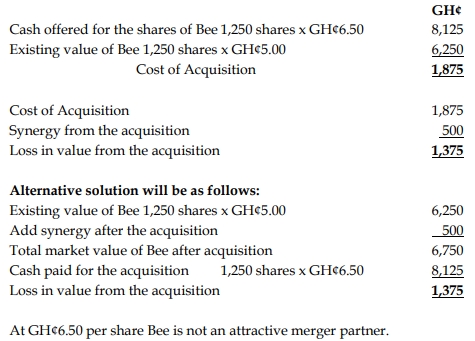
(a) Mama Ltd – Acquisition
NPV and post-acquisition value
Computation of NPV:
The NPV of an acquisition is the gain from the acquisition less the cost of the
acquisition:
The gain from the acquisition is the PV of synergy from the acquisition:
𝐺𝑎𝑖𝑛 (𝑃𝑉 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑦𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦) = ![]()
Cost saving = given as GHS600,000 every year perpetually
As the firm has both equity and debt in its capital structure, the appropriate
cost of capital to use as discount rate is the WACC.
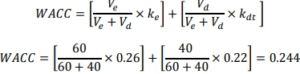
Cost of equity, ke is estimated from the CAPM:
𝑘𝑒 = 𝑟𝑓 + 𝛽𝑖(𝐸(𝑟𝑚) − 𝑟𝑓)
𝑘𝑒 = 0.2 + 1.2(0.05) = 0.26
Cost of the acquisition is the excess of the purchase consideration over the
value of the target:
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 = 𝐶𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑜𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟 − 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑃𝑎𝑝a
𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 = 𝐺𝐻𝑆25,000,000 − 𝐺𝐻𝑆22,500,000 = 𝐺𝐻𝑆2,500,000
The NPV is then computed as Gain less Cost:
𝑁𝑃𝑉 = 𝐺𝑎𝑖𝑛 − 𝐶𝑜𝑠𝑡 = 𝐺𝐻𝑆2,459,016 − 𝐺𝐻𝑆2,500,000 = (𝐺𝐻𝑆40,984)
Advice based on NPV:
The negative NPV suggests that if the acquisition happens, the value of
Mama would reduce by GHS40,984. Therefore, the directors of Mama
should discard the acquisition plan.
b. The value of combined entity:
𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑡 − 𝑎𝑐𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 = 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑀𝑎𝑚𝑎 + 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒𝑃𝑎𝑝𝑎 + 𝑃𝑉 𝑜𝑓 𝑆𝑦𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 − 𝐶𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑜𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟
𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑡 − 𝑎𝑐𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
= 𝐺𝐻𝑆60,000,000 + 𝐺𝐻𝑆22,500,000 + 𝐺𝐻𝑆2,459,016 − 𝐺𝐻𝑆2,500,000
𝑃𝑜𝑠𝑡 − 𝑎𝑐𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 = 𝐺𝐻𝑆82,459,016m
ii) Share exchange ratio (ER)
The number of shares Mama should issue to shareholders of Papa can be
calculated based on market price as under:
![]()
The share exchange ratio between Mama and Papa may be expressed as 3:4
or 0.75:1. That is Mama should issue 3 shares of its ordinary stock for every
4 shares in Papa (or 75 shares of Mama for every 100 shares in Papa).
- Tags: Acquisition valuation, Corporate finance, Mergers and Acquisitions, NPV, Synergy
- Level: Level 3
- Topic: Valuation of acquisitions and mergers
- Series: NOV 2016
- Uploader: Joseph