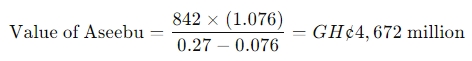- 6 Marks
Question
Zantem Ltd has equity of GH¢10,000,000 while Bonty Ltd has equity of GH¢12,000,000. The two companies are in competition for the same market space. This has increased their advertising and marketing costs. The Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA) has threatened to disallow a portion of their advertising and marketing costs, which appear astronomically high.
The Management of the two companies have invited you, a tax expert, to be part of a discussion to look at the possible ways the two companies can eliminate or reduce any tax exposure to their shareholders with the potential threat from the GRA.
Required:
Advise the Management on the tax strategy(ies) to adopt to reduce their cost while creating value for their shareholders. (6 marks)
Answer
- Merger or Amalgamation: Under section 47 of Act 896, gains arising from a merger, amalgamation, or reorganization are exempt from tax if there is 50% or more continuity in the underlying ownership of the new assets. The two companies should consider merging or amalgamating, provided they will achieve at least 50% in the underlying ownership. Zantem Ltd must increase its capitalization to be at par with Bonty Ltd to avoid tax liabilities on gains.
- Joint Advertising: The companies could consider joint advertising to share costs, thereby reducing the overall expenditure on marketing. This strategy would keep costs down and reduce the potential for GRA disallowing the expenses.
- Reduction or Elimination of Advertising Costs: If feasible, the companies might reduce or eliminate advertising and marketing costs entirely. This could involve leveraging other cost-effective marketing strategies that do not attract the scrutiny of the GRA.
- Topic: Tax planning
- Series: NOV 2023
- Uploader: Theophilus

 (1 mark for each line up to 5, 1 mark each for the growth rate and 2 marks for cost of equity = 8 marks)
(1 mark for each line up to 5, 1 mark each for the growth rate and 2 marks for cost of equity = 8 marks)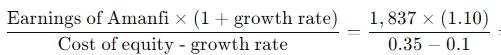 =
=