- 20 Marks
Question
a) The monthly sales of Danamo Company Limited have been given as follows:
| Monthly Sales (GH¢’000) | Moving Total (GH¢’000) |
|---|---|
| April | 150 |
| May | 140 |
| June | 160 |
| July | 180 |
| August | 200 |
| September | 190 |
| October | 220 |
| November | 230 |
| December | 250 |
Required:
i) Using the three-month moving average, calculate the trend. (3 marks)
ii) Using the line of best fit, estimate the sales of January, February, and March of the following year. (12 marks)
b) State and explain FIVE (5) sources of information that may be considered in setting standard prices for materials in Management Accounting. (5 marks)
Answer
a)
i) Three-Month Moving Average
| Month | Sales (GH¢’000) | Moving Total (GH¢’000) | Moving Average (GH¢’000) |
|---|---|---|---|
| April | 150 | – | – |
| May | 140 | 450 | 150 |
| June | 160 | 480 | 160 |
| July | 180 | 540 | 180 |
| August | 200 | 570 | 190 |
| September | 190 | 610 | 203.33 |
| October | 220 | 640 | 213.33 |
| November | 230 | 700 | 233.33 |
| December | 250 | – | – |
| (3 marks evenly spread using ticks) |
ii) Line of Best Fit
| Month (X) | Sales (Y) | XY | X² |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 150 | 150 | 1 |
| 2 | 160 | 320 | 4 |
| 3 | 180 | 540 | 9 |
| 4 | 190 | 760 | 16 |
| 5 | 203 | 1015 | 25 |
| 6 | 213 | 1278 | 36 |
| 7 | 233 | 1631 | 49 |
| Total | 1329 | 5730 | 140 |
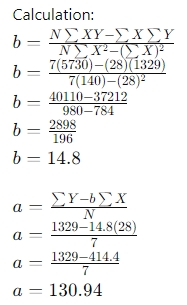
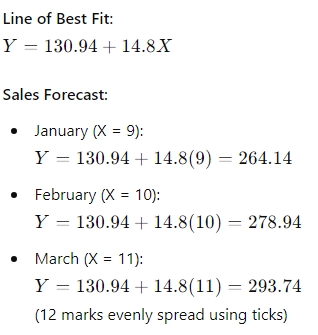
b) Sources of Information for Setting Standard Prices
- Quotations and Estimates from Potential Suppliers: Price quotations or estimates provided by suppliers.
- Trend Information from Past Data: Historical data on material prices and trends.
- Bulk Discounts: Information on discounts for bulk purchases.
- Packaging and Carriage Inwards: Charges for packaging and transportation costs.
- Quality of Material: The expected quality may influence the price.
- Internally Manufactured Components: The predetermined standard cost for components.
(Any 5 points at 1 mark = 5 marks)
- Tags: Forecasting, Moving Average, Standard Prices, Trend Analysis
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Forecasting, Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
- Series: MAY 2020
- Uploader: Joseph
