- 20 Marks
Question
Alokome Plc is a company that produces and sells one product “Iga”. Information relating to the operations of Alokome Plc for the first two months of 2023 is as follows:
i) Iga sells for GH₵500 per unit.
ii) There were no inventories of Iga at the end of December 2022.
iii) Other relevant information is as follows:
| Cost Element | GH₵ |
|---|---|
| Direct material and wages | 220 |
| Variable production overhead | 30 |
Budgeted and actual costs per month:
| Cost Element | GH₵ |
|---|---|
| Fixed production overhead | 990,000 |
| Fixed selling and administrative expenses | 400,000 |
| Variable selling expenses | 12.5% of sales |
Normal capacity: 110,000 units per month
Number of units produced and sold:
| Month | Sales (units) | Production (units) |
|---|---|---|
| January | 128,000 | 140,000 |
| February | 110,000 | 102,000 |
Required:
Using the information above, prepare in a columnar form profit statements for January and February 2023 using:
a) Marginal costing (10 marks)
b) Absorption costing (10 marks)
Answer
a) Alokome Plc – Profit Statement for January and February 2023 (Marginal Costing)
| January (GH₵’000) | February (GH₵’000) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sales revenue | 64,000 | 55,000 |
| Less: Variable cost of sales: | ||
| Beginning inventory | – | 3,000 |
| Production cost | 35,000 | 25,500 |
| Ending inventory | (3,000) | (1,000) |
| Variable cost of production | 32,000 | 27,500 |
| Variable selling expenses | 8,000 | 6,875 |
| Variable cost of sales | (40,000) | (34,375) |
| Contribution | 24,000 | 20,625 |
| Less: Fixed costs | ||
| Fixed production overhead | (990) | (990) |
| Fixed selling and admin. expenses | (400) | (400) |
| Profit | 22,610 | 19,235 |
| (Marks are evenly spread using ticks = 10 marks) |
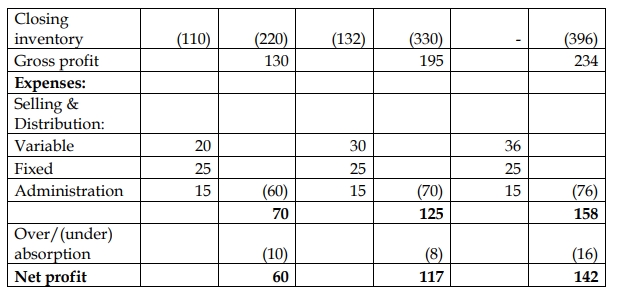
b) Alokome Plc – Profit Statement for January and February 2023 (Absorption Costing)
| January (GH₵’000) | February (GH₵’000) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sales revenue | 64,000 | 55,000 |
| Less: Full cost of sales: | ||
| Beginning inventory | – | 3,108 |
| Production cost | 36,260 | 26,418 |
| Ending inventory | (3,108) | (1,036) |
| Full cost of production | 33,152 | 28,490 |
| Gross profit (Notional) | 30,848 | 26,510 |
| Adjustment for under/over absorption of fixed prodn o/head | 270 | (72) |
| Gross profit (Actual) | 31,118 | 26,438 |
| Less: Selling and administrative expenses: | ||
| Variable selling expenses | (8,000) | (6,875) |
| Fixed selling and admin. expenses | (400) | (400) |
| Profit | 22,718 | 19,163 |
| (Marks are evenly spread using ticks = 10 marks) |
Workings:
| Calculation | GH₵ |
|---|---|
| Variable production cost per unit | |
| Direct material and wages | 220 |
| Variable production overhead | 30 |
| Total | 250 |
| Calculation | GH₵ |
|---|---|
| Fixed production overhead per unit | 9 |
| Full production cost per unit | |
| Direct material and wages | 220 |
| Variable production overhead | 30 |
| Fixed production overhead per unit | 9 |
| Total | 259 |
- Tags: Absorption Costing, Marginal Costing, Over/Under Absorption, Profit Statement
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Marginal Costing and Absorption Costing
- Series: NOV 2023
- Uploader: Joseph