- 20 Marks
Question
a) Inventory refers to the goods and materials that a business holds for the ultimate goal of resale, production, or utilization in the near future. Inventory could be in the form of raw materials, finished goods, work in progress, among others.
Required:
Identify FIVE (5) reasons actual inventory counted may be different from the balance in the inventory records. (5 marks)
Answer
a) Causes of discrepancies in closing inventory:
- Theft by staff
- Evaporation in the case of liquids and gas
- Error in counting
- Casting errors
- Errors in recording
- Over or understatement in stocks issued
- Wrong classifications/coding
- Error in counting at the time of receipt of stocks.
(Any 5 points @ 1 mark each = 5 marks)
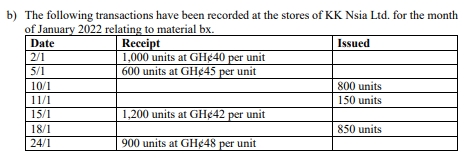
b) Statement of inventory movement (FIFO):
| Date | Receipt | Issued | Balance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2/1/2022 | 1,000 @ GH¢40 | 1,000 @ GH¢40 = GH¢40,000 | |
| 5/1/2022 | 600 @ GH¢45 | 1,000 @ GH¢40 = GH¢40,000 | |
| 600 @ GH¢45 = GH¢27,000 | |||
| 10/1/2022 | 800 @ GH¢40 | 200 @ GH¢40 = GH¢8,000 | |
| 600 @ GH¢45 = GH¢27,000 | |||
| 11/1/2022 | 150 @ GH¢40 | 50 @ GH¢40 = GH¢2,000 | |
| 600 @ GH¢45 = GH¢27,000 | |||
| 15/1/2022 | 1,200 @ GH¢42 | 50 @ GH¢40 = GH¢2,000 | |
| 600 @ GH¢45 = GH¢27,000 | |||
| 1,200 @ GH¢42 = GH¢50,400 | |||
| 18/1/2022 | 850 @ GH¢42 | 50 @ GH¢40 = GH¢2,000 | |
| 600 @ GH¢45 = GH¢27,000 | |||
| 350 @ GH¢42 = GH¢14,700 | |||
| 24/1/2022 | 900 @ GH¢48 | 1,000 @ GH¢42 = GH¢42,000 | |
| 900 @ GH¢48 = GH¢43,200 | |||
| (Marks are evenly spread using ticks = 10 marks) |
c) Sources of management information: Examples
- Internal: Ledger books, invoices, budget statements.
- External: Internet, journals, print media, social media, reports from regulatory bodies.
(2 marks)
d) An investment center is a segment of an organization that has the authority to invest resources of the organization, incur cost, and generate sufficient revenue to pay off the investment in assets. When a firm evaluates an investment center, it looks at the rate of return as measured by ROI and RI that it can earn on its investment.
- Tags: FIFO Method, Inventory Discrepancies, Investment Center, Sources of Information
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Accounting for Inventory and Labour
- Series: DEC 2022
- Uploader: Joseph
