- 20 Marks
Question
Lekker Inc (Lekker) is a film company located in South Africa. The company is planning to expand into other African countries. The research department of Lekker recommends Ghana as a good location for establishing a subsidiary due to its abundant talent and political stability. However, the company is unsure whether to establish a completely new subsidiary or acquire an existing film company in Ghana. You have been engaged as a consultant to guide Lekker in taking this decision.
Your preliminary assessment revealed the following:
i) You have identified a Ghanaian filmmaker who owns a fast-growing film company called Akwaaba Films (Akwaaba). You observed that the Ghanaian filmmaker is likely to sell Akwaaba if Lekker could pay GH¢450,000 as purchase consideration. Akwaaba is entirely self-financed, with the owner receiving all profits as dividends. You forecast that Akwaaba’s profit after tax will grow at a rate of 6% per year for the first two years, 4% per year for the next two years, and thereafter, grow at a constant rate of 2% per year in perpetuity. The financial information extracted from Akwaaba shows the following:
| Description | GH¢ |
|---|---|
| Revenue | 250,000 |
| Operating Cost | (140,000) |
| Administrative cost | (30,000) |
| Profit before tax | 80,000 |
| Tax @ 25% | (20,000) |
| Profit after tax | 60,000 |
ii) If Lekker decides to set up the subsidiary in Ghana by itself with the same GH¢450,000 purchase consideration for Akwaaba, its after-tax cash flows will be as follows:
| Year | Cash Flow (GH¢) |
|---|---|
| Year 1 | 15,000 |
| Year 2 | 26,000 |
| Year 3 | 35,000 |
| Year 4 | 33,000 |
The overall Price/Earnings (P/E) ratio for the film industry in Ghana is 15 times. The average cash flow risk for unquoted companies in Ghana is 20%. Lekker does not intend to list on the Ghana Stock Exchange.
iii) Lekker’s cost of capital is 16%.
Required:
a) Enumerate THREE (3) advantages of expansion through acquisition over organic expansion to the owners of Lekker. (6 marks)
b) Compute the value of Akwaaba using the dividend valuation method and advise Lekker whether it should acquire Akwaaba at the purchase consideration of GH¢450,000. (8 marks)
c) Using the P/E ratio method, estimate the expected value of Lekker’s subsidiary in Ghana without the acquisition. (4 marks)
d) State TWO (2) reasons mergers and acquisitions may fail to achieve the expected outcomes. (2 marks)
Answer
a) Three Advantages of Expansion Through Acquisition Over Organic Expansion:
- Speed of Market Entry:
Acquiring an existing company like Akwaaba allows Lekker to enter the Ghanaian market quickly, without the delays associated with setting up a new subsidiary from scratch. - Established Market Presence:
Through acquisition, Lekker would gain immediate access to Akwaaba’s existing customer base, established brand, and market relationships, which would take time to develop through organic growth. - Lower Risk:
Acquiring an existing, successful company like Akwaaba reduces the risk associated with entering a new market, as the business model, management team, and market strategy are already proven.
(6 marks)
b) Value of Akwaaba Using the Dividend Valuation Model:
The Dividend Valuation Model (DVM) can be used to value Akwaaba based on its expected future profits:
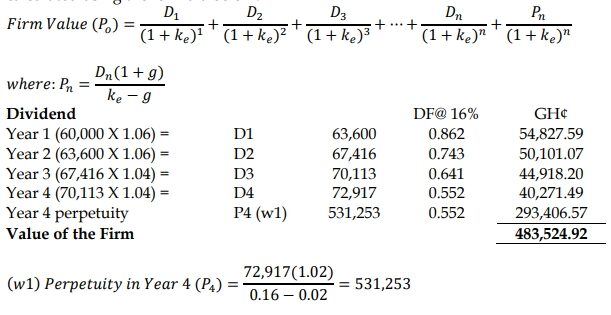
Note that the perpetuity is calculated from Year 4 onwards, therefor the discount
factor is the same as that of Year 4 and not Year 5
Conclusion: the purchase consideration of GH¢450,000 quoted by the Ghanaian
filmmaker is lower than the value of the firm, leading to a net gain of 33,524.92.
Based on this Lekker Inc. should purchase Akwaaba Inc
c) Expected Value of Lekker’s Subsidiary Using the P/E Ratio Method:

d) Two Reasons Mergers and Acquisitions May Fail to Achieve Expected Outcomes:
- Cultural Integration Issues:
Differences in corporate cultures can lead to conflicts and inefficiencies post-merger, hampering the realization of expected synergies. - Overvaluation of Target Company:
If the acquiring company overestimates the value of the target company, the merger may not deliver the anticipated financial benefits, leading to losses.
(2 marks)
- Tags: Acquisition strategy, Expected outcomes, Mergers, P/E Ratio, Valuation
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Business valuations, Mergers and acquisitions
- Series: NOV 2023
- Uploader: Theophilus
