- 20 Marks
Question
Zed Ltd is considering the immediate purchase of some, or all, of the share capital of one of two firms—Fasco Ltd and Boscan Ltd. Both Fasco Ltd and Boscan Ltd have one million ordinary shares issued, and neither company has any debt capital outstanding.
Both firms are expected to pay a dividend in one year’s time—Fasco’s expected dividend amounting to 30p per share, and Boscan’s being 27p per share. Dividends will be paid annually and are expected to increase over time. Fasco’s dividends are expected to display perpetual growth at a compound rate of 6% per annum. Boscan’s dividend will grow at the high annual compound rate of 33⅓% until a dividend of 64p per share is reached in year 4. Thereafter, Boscan’s dividend will remain constant.
If Zed is able to purchase all the equity capital of either firm, then the reduced competition would enable Zed to save some advertising and administrative costs, which would amount to GH¢225,000 per annum indefinitely, and, in year 2, to sell some office space for GH¢800,000. These benefits and savings will only occur if a complete takeover is carried out. Zed would change some operations of any company completely taken over, the details are:
- Fasco – No dividend would be paid until year 3. Year 3 dividend would be 25p per share, and dividends would then grow at 10% per annum indefinitely.
- Boscan – No change in total dividends in years 1 to 4, but after year 4, dividend growth would be 25% per annum compound until year 7. Thereafter, annual dividends would remain constant at the year 7 amount per share.
An appropriate discount rate for the risk inherent in all the cash flows mentioned is 15%.
Required:
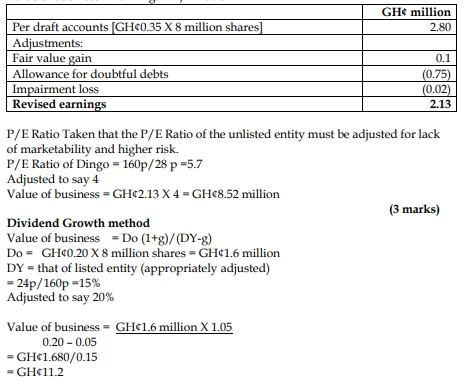
a) Calculate the valuation per share for a minority investment in each of the firms, Fasco and Boscan, which would provide the investor with a 15% rate of return. (6 marks)
b) Calculate the maximum amount per share which Zed should consider paying for each company in the event of a complete takeover. (8 marks)
c) Comment on any limitation of the approach used in part (a), and specify the other major factors which would be important to consider if the proposed valuations were being undertaken as a practical exercise. (6 marks)
Answer
Valuation per share for a minority investment
Using the dividend valuation model (DVM), the value of ordinary shares is given by:

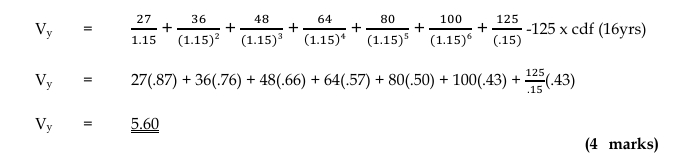
c) Limitations of the Approach
- Dividend Growth Assumptions: The dividend valuation model assumes that dividends grow at a constant rate indefinitely, which may not hold in real-life scenarios. Boscan’s variable dividend growth complicates the model.
- Market Conditions: The model does not account for the short-term market factors or price-earnings ratio that may affect stock prices.
- Synergies: The assumed synergies and cost savings may not materialize in practice, affecting the overall valuation.
Other factors to consider include:
- Management changes after acquisition.
- Competitive responses in the market.
- Financing options and capital structure post-acquisition.
- Tags: Acquisition, Discount rate, Dividend Growth, Synergies, Valuation
- Level: Level 3
- Topic: Valuation of acquisitions and mergers
- Series: NOV 2017
- Uploader: Dotse