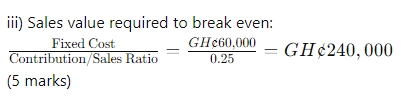- 20 Marks
Question
HEALTH-GRACE limited produces one standard product called Bambino Syrup which sells at ₦20.00 per bottle. The trading results for the six months ended June 30, 2015 were as follows:
| Month | Sales (Units) | Profit / Loss (₦) |
|---|---|---|
| January | 120,000 | 80,000 |
| February | 140,000 | 120,000 |
| March | 60,000 | (40,000) |
| April | 96,000 | 32,000 |
| May | 104,000 | 24,000 |
| June | 72,000 | 16,000 |
From the above information, you are required to calculate the following:
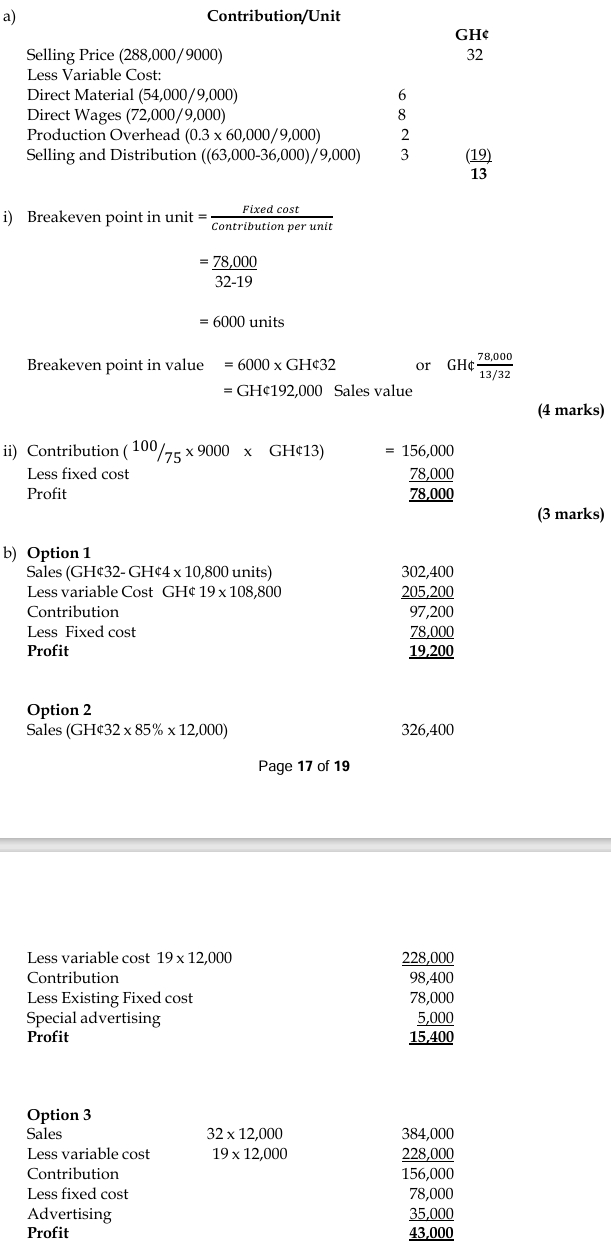
a. Break-even point in units and Naira value. (2 Marks)
b. Fixed cost. (2 Marks)
c. Variable cost per unit. (8 Marks)
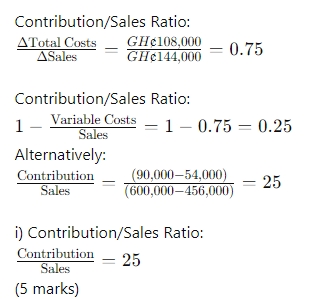
d. Profit volume ratio. (2 Marks)
e. Contribution, assuming 70,000 bottles are sold. (2 Marks)
f. Margin of safety assuming 90,000 bottles are sold. (1 Mark)
g. The number of bottles to be sold to generate a profit after tax of ₦70,000 assuming the tax rate is 30%. (3 Marks)
Answer
a. Break-even point in units = Total fixed cost / contribution per unit = N160,000/ (20 – 18) = 80,000 units
Break-even point in value = Total fixed cost / contribution Margin Ratio = N160,000/ (2 / 20) = N1,600,000
b. Fixed cost: Fixed Cost = ₦1,600,000
c. Variable cost per unit:
Using High and Low Methods
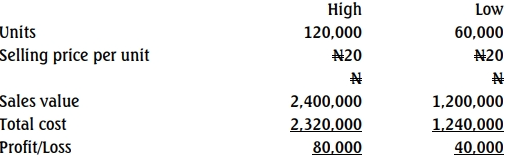
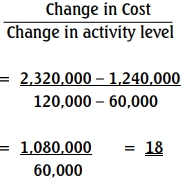
Variable cost per unit = N18
d. Profit volume ratio: Profit / Volume Ratio = 2 / 20 x 100 = 10%
e. Contribution, assuming 70,000 bottles are sold: 70,000 x N2 = N140,000
f. Margin of safety assuming 90,000 bottles are sold: 90,000 – BEP in units = 90,000 – 80,000 = 10,000 units
g. The number of bottles to be sold to generate a profit after tax of ₦70,000 assuming the tax rate is 30%:
Sales in units = (Total fixed cost + target profit) / contribution per unit
Target profit = N70,000 / 30% = N233,333
Sales in units = (N160,000 + N233,333)/2 = 196,667 bottles
- Tags: Break-even Analysis, CVP Analysis, Marginal Safety, Profitability
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
- Series: MAY 2016
- Uploader: Joseph