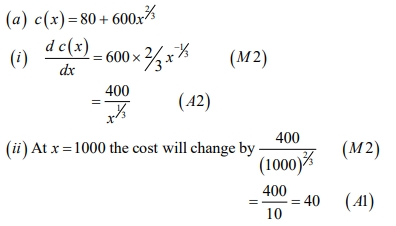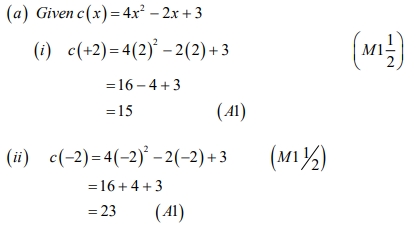- 12 Marks
Question
Kyerewaa Ventures is a manufacturing company in the business of producing beverage cans for clients in the brewery industry. The weekly total cost to produce xx cans is given by:
![]()
The demand function for the cans is given by:
P(x) = 200 − 0.005x
The company has set a production limit to 10,000 cans and it sells all the cans that are produced.
Required:
i) Derive an expression for marginal cost, marginal revenue, and marginal profit. (4 marks)
ii) Determine the cost, revenue, and profit when the 2,501st can is produced and sold. (3 marks)
iii) Determine the cost, revenue, and profit when the 7,501st can is produced and sold. (3 marks)
iv) Advise the company whether to produce the 2,501st can or the 7,501st can. (2 marks)
Answer


- Tags: Cost Function, Marginal Cost, Marginal Profit, Marginal Revenue, Optimization, Revenue Function
- Level: Level 1
- Series: NOV 2017
- Uploader: Theophilus