- 5 Marks
Question
Ape has 2,500 shares outstanding at GH¢10 per share. Bee has 1,250 shares outstanding at GH¢5 per share. Ape estimates that the value of synergistic benefit from acquiring Bee is GH¢500. Bee has indicated that it would accept a cash purchase offer of GH¢6.50 per share.
Required:
Identify whether Ape should proceed with the merger
Answer
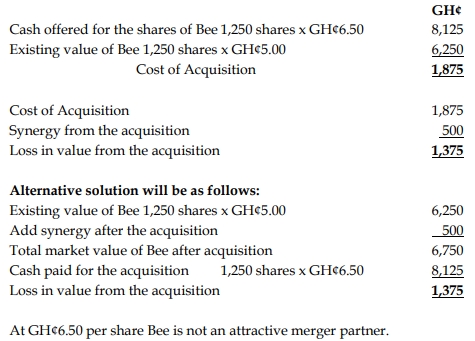
Since the net loss from the acquisition is GH¢1,375, Ape should not proceed with the merger as it results in a financial loss despite the synergy benefits.
- Tags: Acquisition, Cash Purchase, Corporate Strategy, Mergers, Share Valuation, Synergy
- Level: Level 3
- Topic: Valuation of acquisitions and mergers
- Series: MAY 2019
- Uploader: Theophilus
