- 20 Marks
Question
From the information given below, you are required to compute the price of store issues and the value of closing stocks using:
i. First-In-First-Out (FIFO) basis
ii. Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) basis
- January 2nd: Purchased 500 Units of XYZ at N40 per unit
- January 7th: Purchased 200 Units at N45 per unit
- January 10th: Issued 300 Units
- January 12th: Purchased 350 Units at N42 per unit
- January 15th: Issued 500 Units
- January 18th: Purchased 200 Units at N38 per unit
Answer
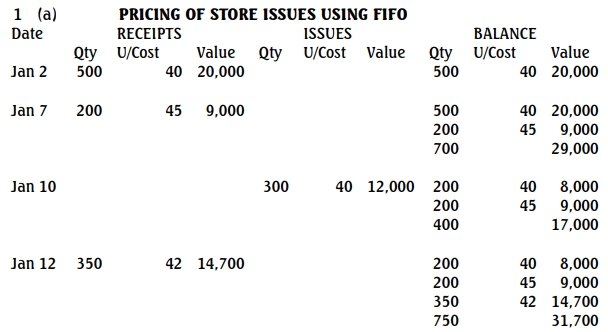
a. Pricing using FIFO:
- On January 10, 300 units are issued at N40 (first purchase price).
- On January 15, 200 units are issued at N40 (from remaining January 2 stock) and 200 units at N45 (from January 7 stock), and 100 units at N42 (from January 12 purchase).
- Closing stock: The closing stock consists of 250 units at N42 and 200 units at N38.
The closing stock value using FIFO is N18,100.
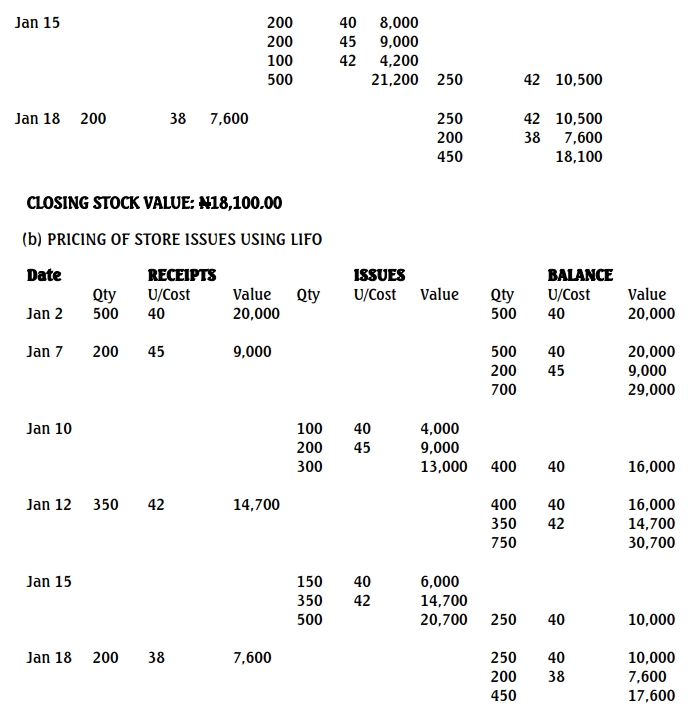
b. Pricing using LIFO:
- On January 10, 300 units are issued at N45 (most recent purchase).
- On January 15, 350 units are issued at N42 (from January 12 purchase), and 150 units at N40 (from January 2 stock).
- Closing stock: The closing stock consists of 250 units at N40 and 200 units at N38.
The closing stock value using LIFO is N17,600.
Explanation: FIFO assumes that the first goods purchased are the first ones sold, so the closing stock reflects the most recent purchases. LIFO assumes that the last goods purchased are the first ones sold, so the closing stock reflects the older purchase prices.
- Tags: Closing Stock, FIFO, LIFO, Pricing methods
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Costing Methods
- Series: MAY 2024
- Uploader: Dotse

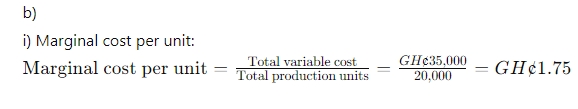 Profit Statement (Marginal Costing):
Profit Statement (Marginal Costing): Profit Statement (Absorption Costing):
Profit Statement (Absorption Costing):