- 20 Marks
Question
Sabir Company is considering whether to invest in a project whose details are as follows.
The project will involve the purchase of equipment costing GH¢2,000,000. The equipment will be used to produce a range of products for which the following estimates have been made.
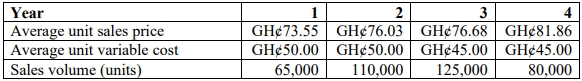
Incremental fixed costs are GH¢1,200,000 per annum. The sales prices allow for expected price increases over the period. However, cost estimates are based on current costs and do not allow for expected inflation in costs. Inflation is expected to be 3% per year for variable costs and 4% per year for fixed costs. The incremental fixed costs are all cash expenditure items. Tax on profits is at the rate of 30%, and tax is payable in the same year in which the liability arises.
Sabir Company uses a four-year project appraisal period, but it is expected that the equipment will continue to be operational and in use for several years after the end of the first four-year period.
The company’s cost of capital for investment appraisal purposes is 10%. Capital projects are expected to pay back within two years on a non-discounted basis and within three years on a discounted basis. Tax allowable depreciation will be available on the equipment at the rate of 25% per year on a reducing balance basis. Any balancing allowance or balancing charge is not attributed to a project unless the asset is actually disposed of at the end of the project period.
Required:
a) Calculate the net present value (NPV) of the project.
(11 marks)
b) To the nearest month, calculate the non-discounted payback period and the discounted payback period.
(4 marks)
c) Explain the meaning of market volatility in financial markets.
(3 marks)
d) Explain the difference between a bull and bear market.
(2 marks)
Answer
a) Workings
Year Written down value
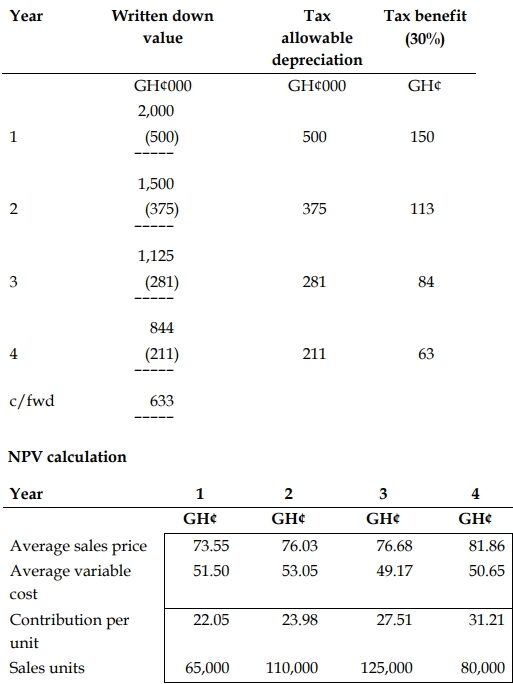
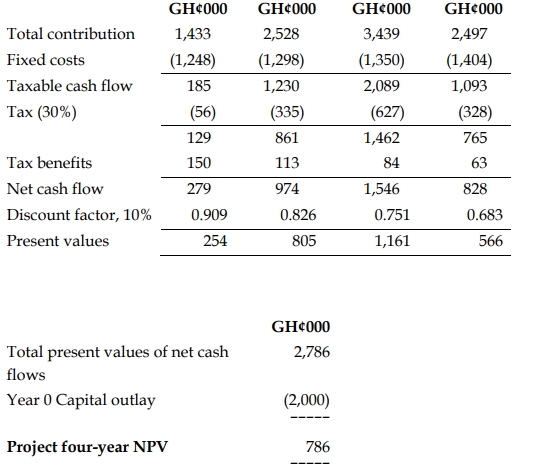
Total Present Value of Net Cash Flows: GH¢2,786,000
Year 0 Capital Outlay: GH¢2,000,000
Project Four-Year NPV: GH¢786,000
b) Payback and Discounted Payback
| Year | Cash Flow (GH¢’000) | Cumulative Cash Flow (GH¢’000) | Discounted Cash Flow (GH¢’000) | Cumulative Discounted Cash Flow (GH¢’000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | (2,000) | (2,000) | (2,000) | (2,000) |
| 1 | 279 | (1,721) | 254 | (1,746) |
| 2 | 974 | (826) | 805 | (1,007) |
| 3 | 1,546 | 720 | 1,161 | 154 |
| 4 | 828 | 1,548 | 566 | 720 |
Non-discounted Payback Period: 2 years + [(826/1,546) × 12] = 2 years 6 months
(2 marks)
Discounted Payback Period: 2 years + [(1,007/1,161) × 12] = 2 years 10 months
(2 marks)
c) Market Volatility Explanation:
Market volatility in financial markets is a measure of the extent to which the price of a financial security (such as a share’s market price), or a market as a whole, or an interest rate, or a currency, or a commodity changes over time. High volatility means rapid and large changes in a price or rate over a short period of time. Low volatility means smaller and less frequent price changes.
Volatility refers to price movements in both directions, up and down. If prices move over time always in the same direction (either up or down, but not both), this does not mean high volatility. Volatility implies uncertainty about the way that prices will move next, and by how much. High volatility creates high financial risk. Investors will want higher returns to invest in financial instruments where price volatility is high.
(3 marks)
d) Bull and Bear Markets Explanation:
In a bull market, prices on the whole move upwards continually over time. For example, in a bull stock market, share prices on the whole continue to rise over time.
In a bear market, prices on the whole move downwards continually over time. For example, in a bear stock market, share prices on the whole continue to fall over time.
(2 marks)
- Topic: Discounted cash flow, Introduction to Investment Appraisal
- Series: MAY 2020
- Uploader: Theophilus
