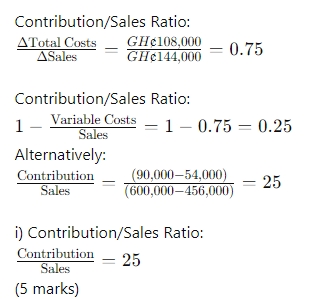
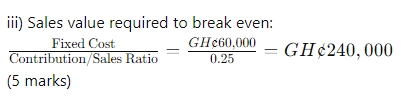- 20 Marks
Question
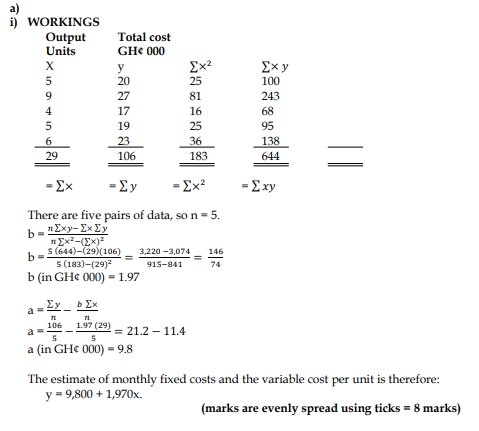
a) Total production costs each week in a production department have been measured for the past five weeks, as follows:
| Week | Units Produced | Total Cost (GH¢000) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 20 |
| 2 | 9 | 27 |
| 3 | 4 | 17 |
| 4 | 5 | 19 |
| 5 | 6 | 23 |
Required:
i) Use linear regression analysis to obtain an estimate of fixed costs per week and the variable cost of production per unit (see formula table). (8 marks)
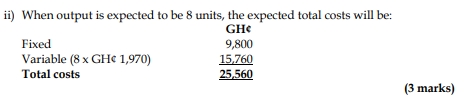
ii) Use your results to estimate total costs in a week when 8 units are produced. (3 marks)
iii) Explain why the regression analysis method of separating cost is considered more accurate than the high-low method. (4 marks)
b) The cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis, also commonly known as breakeven analysis, looks to determine the breakeven point for different sales volumes and cost structures, which can be useful for managers making short-term business decisions. For CVP analysis to be effective, several assumptions are usually made.
Required:
State FOUR (4) assumptions underlying cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis. (5 marks)
Answer
iii) Explanation:
Regression analysis is more accurate than the high-low method because the regression equation estimates costs using information from ALL observations, whereas the high-low method uses only TWO observations. This method measures the difference between actual cost and estimated cost for each observation.
(4 marks)
b) Assumptions underlying breakeven (CVP) analysis:
- Cost can be classified into fixed and variable elements only.
- Variable cost may vary proportionately with the level of activity attained.
- Activity is the only factor that drives cost of production.
- Selling price of the product remains constant.
- Stock levels do not change with activity level.
- Level of technology remains constant.
(Any 4 points @ 1.25 marks each = 5 marks)
- Topic: Cost Segregation and Estimation, Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
- Series: DEC 2022
- Uploader: Joseph