- 3 Marks
Question
Drogo uses the Throughput Accounting technique for efficient allocation of scarce resources. In the second quarter of 2021, the throughput per bottleneck resource for its three products were given as follows:
- Product A: GH¢4
- Product B: GH¢6
- Product C: GH¢9
The total factory cost was GH¢67,500, and the bottleneck resource was 15,000 machine hours.
Required:
Calculate and comment on the Throughput Accounting Ratios of the three products. (3 marks)
Answer
Throughput Accounting Ratio (TPAR) is a relative measure that shows how many times the throughput per limited resource can cover the factory cost per limited resource. The formula for TPAR is:
TPAR=![]()
Calculation:
- Factory cost per bottleneck resource:
Factory cost per bottleneck=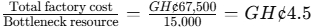
- TPAR for Product A: TPAR=
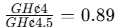
- TPAR for Product B: TPAR=
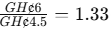
- TPAR for Product C: TPAR=
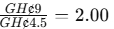
Comment:
- Product A: TPAR is less than 1 (0.89), indicating that Product A is not profitable as its throughput cannot cover the factory cost per bottleneck resource.
- Product B: TPAR is greater than 1 (1.33), suggesting that Product B is profitable.
- Product C: TPAR is the highest (2.00), indicating that Product C is the most profitable among the three products.
- Tags: Bottleneck Resources, Profitability analysis, Throughput Accounting
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Advanced variance analysis
- Series: APR 2023
- Uploader: Joseph
