- 20 Marks
Question
a) Osiadan Contractors Ltd plans to construct housing units in the Kpone-Katamanso District of Ghana for sale to young professionals. It has obtained a US$4 million loan facility from the International Finance Corporation (IFC). The total principal granted will be released in two equal tranches: the first tranche to be released now and the second tranche at the beginning of the fourth year. Interest will be charged on the loan at 12% per annum with semi-annual compounding. The total principal granted plus the total interest is to be paid at the end of the duration of the loan in six years’ time.
To raise money toward the settlement of the maturity value of the loan, Osiadan Contractors Ltd plans to establish a sinking fund by which it will deposit equal amounts of U.S. dollars at the beginning of every quarter starting from the third year until the end of the loan duration. The dollar deposits will be invested at 8% per annum with quarterly compounding.
Required:
i) Compute the maturity value of the loan at the end of six years. (3 marks)
ii) Compute the size of the quarterly deposits to be invested in the sinking fund to raise the amount needed to settle the maturity value of the loan. (4 marks)
iii) Compare and contrast annuity due and ordinary annuity. (3 marks)
b) Klessy Beverages Inc (Klessy), an American malt drink producer, imports barley from Australia and pays for the import in Australian dollars. It has bought a consignment of barley with an invoice value of AUD2.5 million, and payment is due next month. The exchange rate between the United States dollar (USD) and the Australian dollar (AUD) is currently trading at USD0.7265/AUD. The Managers of Klessy fear that the Australian dollar may strengthen against the US dollar. The Treasury Manager has recommended using currency options to address the potential currency risk.
Below are the CME Group’s quotations for weekly options on the Australian dollar:
| Contract Specification | Call | Put |
|---|---|---|
| Contract size | AUD100,000 | AUD100,000 |
| Premium (US$) | 0.0131 | 0.0031 |
| Strike price (US$) | 0.7275 | 0.7275 |
| Expiration | Week 4 | Week 4 |
Required:
i) Justify which option Klessy should buy considering its underlying currency exposure. (3 marks)
ii) Compute the intrinsic value of your selected option and interpret the results. (4 marks)
iii) Distinguish between option premium and option strike (or exercise) price. (3 marks)
Answer
a)
i) Computation of the maturity value of the loan at the end of six years:
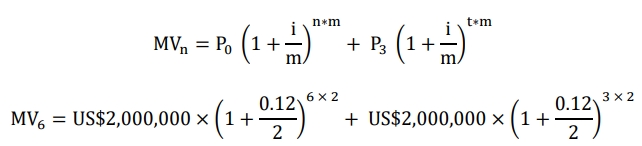
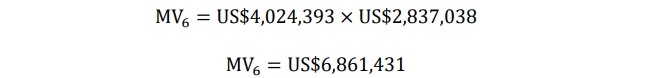
ii) Computation of the size of the quarterly deposits into the sinking fund:
The objective of the sinking fund is to raise money to settle the maturity value of the loan in six years’ time. The future value of the fund (F) should be equal to the maturity value of the loan:
F6 = MV6 = US$6,861,431
As the deposits are to be made at the beginning of each period, this case is an annuity due. The future value formula of an annuity due is used:
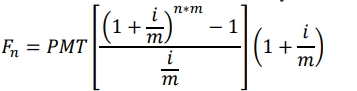
Where:
- Future value = US$6,861,431
- Annual interest rate,i=8%
- Investment period, n=4 years (year 3 to year 6)
- Frequency, m=4
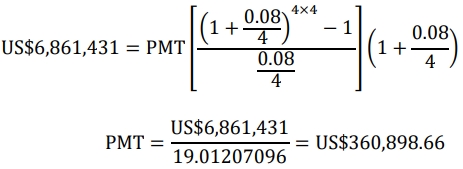
iii) Comparing and contrasting annuity due and ordinary annuity:
Annuity due and ordinary annuity are both forms of a series of equal cash flows. They are similar in the amount of cash flows in the series and the time interval between the cash flows. In both cases, the cash flows are equal in size and occur within the same time interval (e.g., monthly, quarterly).
The difference between the two lies in the timing of the cash flows:
- Annuity Due: Cash flows occur at the beginning of each period.
- Ordinary Annuity: Cash flows occur at the end of each period.
(Marks allocation: 3 marks)
b)
i) Justify the type of option Klessy should buy:
A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at an agreed price before or on the expiration date. In contrast, a put option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at an agreed price before or on the expiration date. Klessy should buy call options on the Australian dollar. Klessy needs to buy the Australian dollar next month to settle the invoice value of the consignment of barley bought. Thus, it needs to buy call options to get the right to buy the Australian dollar at the quoted strike price.
(Marks allocation: 3 marks)
ii) Computation and interpretation of the intrinsic value of the call option:
The intrinsic value of a call option is the maximum of the spot price minus the strike price and zero:
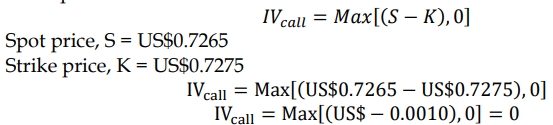
The intrinsic value of the call option is zero, meaning the call option is currently out-of-the-money and will not be profitable to exercise now.
(Marks allocation: 4 marks)
iii) The distinction between option premium and option strike price:
- Option Premium: The price paid for the right to trade the underlying asset at a given strike price before or on a specified expiration date. For example, Klessy would have to pay US$0.0131 to obtain the right to buy one Australian dollar.
- Option Strike Price: The agreed price for the underlying asset. If Klessy buys the call option and elects to exercise the option, it will pay US$0.7275 for every Australian dollar in the contract. The premium is payable when the option contract is bought, while the strike price is payable later when the option is exercised, and the asset is traded.
(Marks allocation: 3 marks)
- Tags: Annuity due, Loan maturity value, Ordinary annuity, Sinking Fund
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Discounted cash flow, Simple interest and compound interest
- Series: JULY 2023
- Uploader: Theophilus
