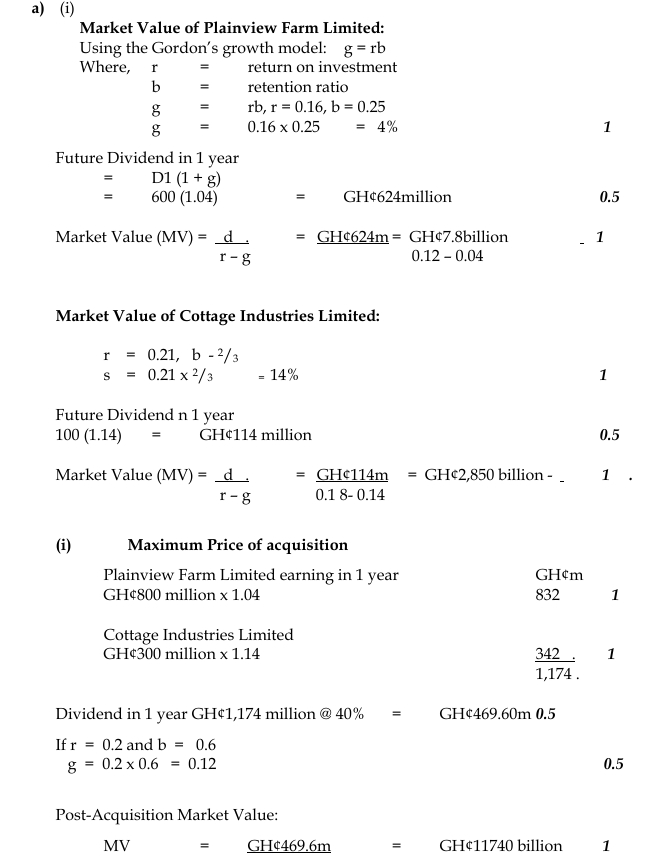
- 8 Marks
Question
Despite substantial evidence, drawn from different countries and different time periods, that suggests the wealth of shareholders in a bidding company is unlikely to be increased as a result of taking over another company, takeovers remain an important part of the business landscape.
Required:
i) Explain briefly when a takeover will make economic and financial sense.
(3 marks)
ii) Discuss briefly FIVE (5) reasons why a takeover may fail to deliver an expected increase in wealth for the bidding company’s shareholders.
(5 marks)
Answer
i) When a takeover makes economic and financial sense
A takeover makes economic and financial sense when it creates value through synergies. The value of the combined business must exceed the sum of the values of the individual businesses. This can be expressed as:
PV Combined business > PV Bidding business + PV Target business
This means that the takeover should generate benefits such as cost savings, revenue enhancement, or improved efficiency, which would not have been realized if the companies operated independently. The combined entity should deliver a higher net present value (NPV) or enhanced future cash flows, justifying the merger or acquisition.
(3 marks)
ii) Five reasons why a takeover may fail to deliver the expected increase in wealth for the bidding company’s shareholders
- Overpayment for the target company:
Management of the bidding company may pay too much for the target company. Often, a premium is paid to convince shareholders of the target to sell their shares. This premium might not be justified by the future gains from the merger, leading to wealth transfer from the bidding company’s shareholders to the target’s shareholders. - Hidden problems in the target company:
Problems that were hidden or undiscovered during the due diligence process may emerge after the acquisition. These issues could be financial, operational, or legal, and they may erode the anticipated benefits from the takeover. - Integration challenges:
Integrating the operations, culture, and management of the two companies may prove difficult. Differences in organizational cultures, management styles, and systems can lead to inefficiencies and prevent the realization of expected synergies. - Management complacency:
After the takeover, management may become complacent, believing that the takeover itself guarantees success. Without continuous effort to integrate and improve operations, the anticipated benefits may not materialize, leading to underperformance. - Errors in valuing the target company:
Misjudgment in valuing the target company may lead to the bidding company overpaying for the acquisition. This often results from incorrect assumptions about future cash flows or failure to account for the risk associated with the acquisition.
- Tags: Acquisitions, Corporate Strategy, Mergers, Shareholder Wealth, Takeover
- Level: Level 3
- Topic: Acquisitions and mergers versus other growth strategies
- Series: NOV 2018
- Uploader: Theophilus