- 20 Marks
Question
The Board of Peartek Ltd is considering the company’s capital investment options for the coming year, and is evaluating the following potential investments:
Investment A:
- Investment of GH¢60,000, including GH¢40,000 for capital equipment and GH¢20,000 for increases in working capital.
- Expected sales of 10,000 units next year with a sales price of GH¢10 and variable costs of GH¢6 per unit.
- Sales price is expected to decline by 20% per annum due to competition, sales volume to fall by 10%, and variable costs to decline by 20%.
- Overheads of GH¢15,000 annually, including a GH¢4,000 depreciation charge.
- The project will be wound up in year three, with working capital recovered and capital equipment sold off for 25% of its cost.
Investment B:
- Immediate outlay of GH¢90,000, financed by borrowing at 6%.
- Expected net profits of GH¢12,000 next year, rising by 3% per annum indefinitely.
Investment C:
- Outlay of GH¢25,000 financed by retained profits.
- Expected annual net cash profits:
- Years 1 to 4: GH¢3,000
- Years 5 to 7: GH¢5,000
- From year 8 onwards: GH¢7,000 in perpetuity.
The company discounts projects lasting 10 years or less at 10%, and others at 13%. Ignore taxation.
Required:
a) As a financial management analyst, you have been asked to advise the board of Peartek Ltd (in the form of a briefing report) which investment should be undertaken. Use the NPV method in your analysis. (15 marks)
b) Minority of board members feel that the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) should also be used as either an alternative or a complementary method of investment appraisal. Calculate the IRR of investments A and B and comment accordingly. (5 marks)
Answer
a) Net Present Value (NPV) Analysis (15 marks):
Investment A:
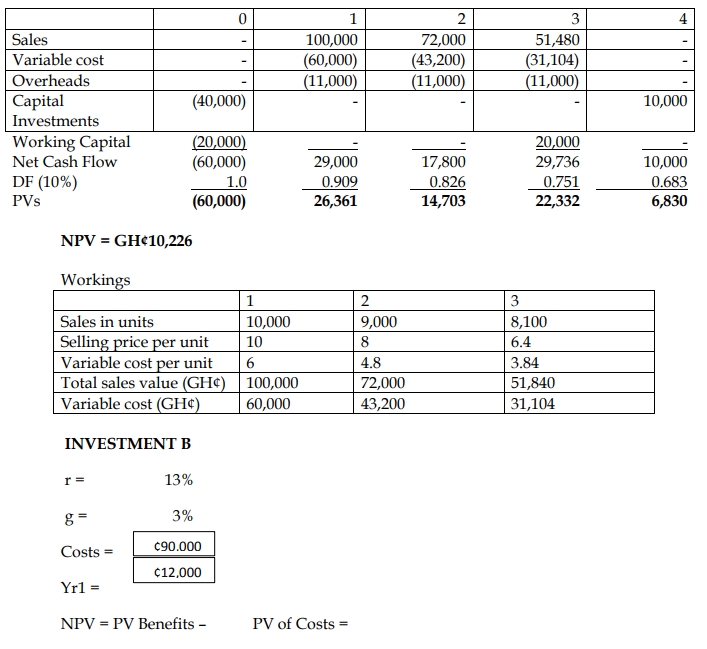
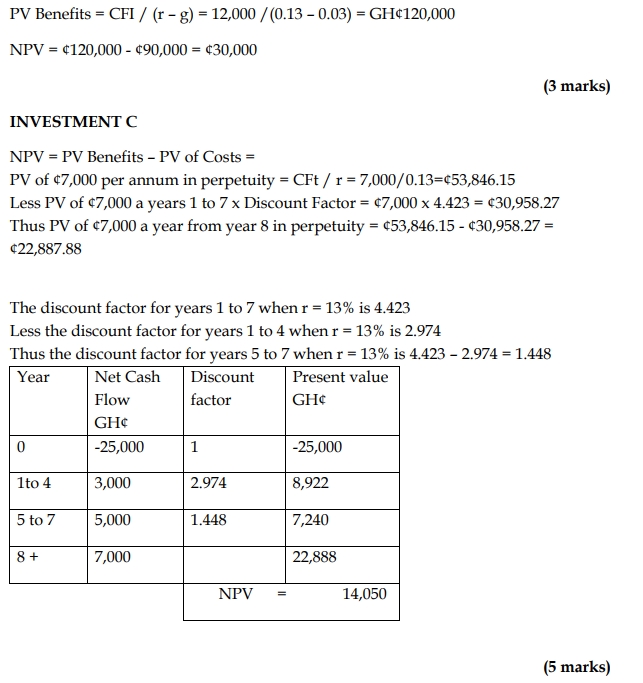
Recommendation:
All projects have positive NPVs and should be undertaken, but Investment B is the most attractive with the highest NPV (GH¢30,000), followed by Investment A and Investment C.
b) Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Analysis (5 marks):
Investment A:
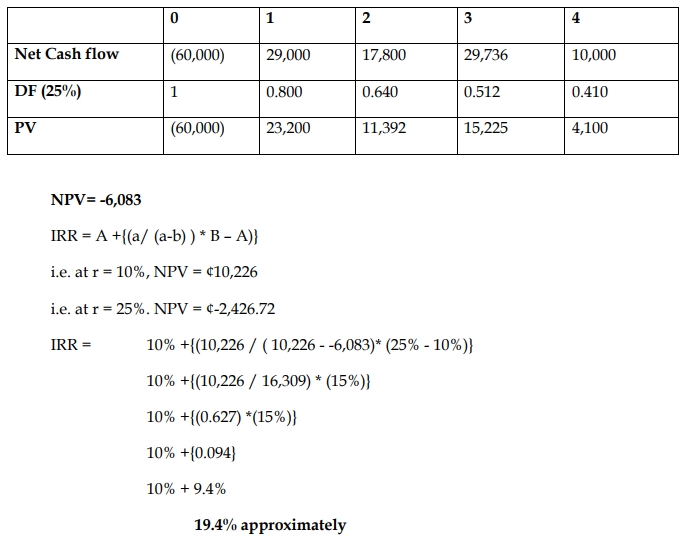
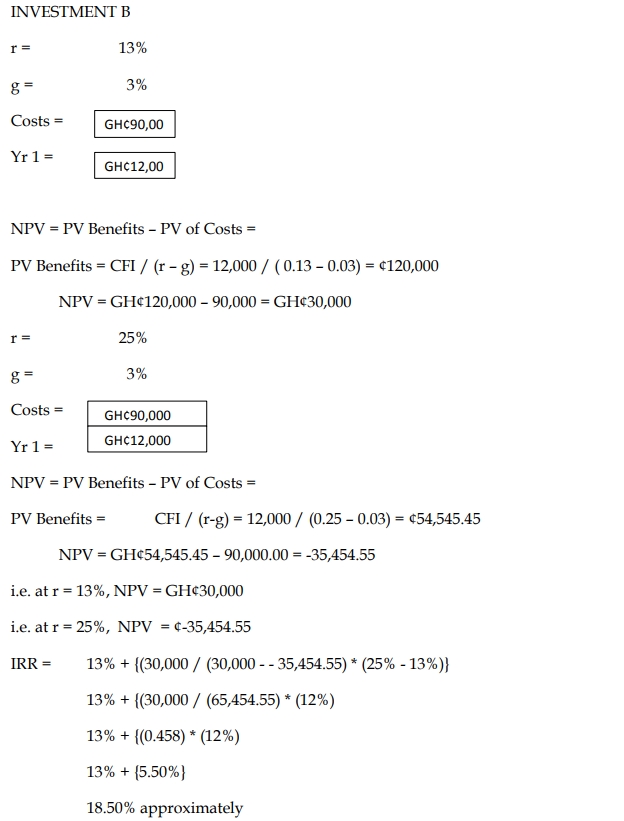
Conclusion:
Both Investment A and Investment B have IRRs above their required rates of return (10% for A and 13% for B). Investment A has a higher IRR (19.4%) than B (18.5%), but Investment B remains more favorable due to its higher NPV.
- Uploader: Theophilus
