- 20 Marks
Question
a) Monetary policies are seen either as expansionary or contractionary depending on the level of growth within the economy. The Bank of Ghana, which is responsible for pursuing sound monetary policies, has recently raised the monetary policy rate by 150 basis points.
Required:
i) In reference to the statement above, distinguish between expansionary monetary policy and contractionary monetary policy. (4 marks)
ii) Would you describe the raise in the monetary policy rate as an expansionary or contractionary monetary policy action? Explain. (2 marks)
iii) Explain TWO (2) implications of raising the monetary policy rate for the financial performance of businesses. (4 marks)
b) Moli Ltd is financed by a mixture of equity and debt capital in the ratio of 2:1. The pre-tax cost of debt is 25% whilst the risk-free interest rate is 15%. The available market information puts the average stock market return on equity at 22%. The equity beta value of Moli Ltd has been estimated as 0.9. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
Required:
i) Calculate the cost of equity. (4 marks)
ii) Calculate the weighted average cost of capital. (6 marks)
Answer
a)
i) Distinction between Expansionary and Contractionary Monetary Policy:
- Expansionary Monetary Policy:
This policy lowers interest rates and expands money supply to stimulate economic activities and encourage spending, which would increase inflation to a desired level in the long term. It is typically employed during periods of slow economic growth or recession to boost the economy. - Contractionary Monetary Policy:
This policy increases interest rates and limits the money supply to slow down economic activities, which would reduce inflation to a desired level in the long term. It is typically employed during periods of high inflation or overheated economic growth to cool down the economy.
(4 marks)
ii) Analysis of the Monetary Policy Rate Increase:
- The Bank of Ghana’s raise in the monetary policy rate by 150 basis points is a contractionary monetary policy action. The increase in the rate is aimed at reducing inflation by increasing the cost of borrowing, thereby discouraging spending and investment.
(2 marks)
iii) Implications of Raising the Monetary Policy Rate:
- Increased Borrowing Costs:
Higher interest rates result in increased borrowing costs for businesses, leading to higher expenses and reduced profitability. - Reduced Consumer Spending:
Higher interest rates can discourage consumer borrowing and spending, leading to reduced demand for goods and services, which can negatively impact business revenues.
(4 marks)
b)
i) Calculation of Cost of Equity:
Cost of equity
re = rf + B(rm-rf)
= 15% + 0.9 (22% – 15%)
= 21.3%
ii) Calculation of Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC):
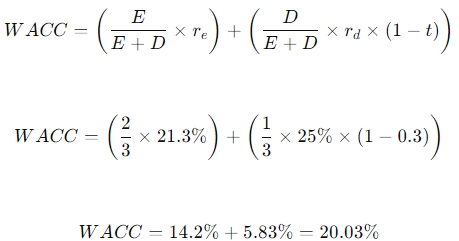
- Topic: Cost of capital, Economic and regulatory environment
- Series: NOV 2023
- Uploader: Theophilus
