- 15 Marks
Question
a) The directors of Clear Tel Ltd, a private telecommunication company, are considering a proposed resolution for converting the company to a public company and listing its equity stock on the stock exchange. The directors expect that the stock market listing can enhance Clear Tel’s ability to raise large amounts of capital from the public. However, they fear that stock market inefficiencies could have a negative effect on the price of Clear Tel’s equity stock.
Required:
Explain the THREE degrees of stock market efficiency, and how the price of Clear Tel is expected to move in each case.
(6 marks)
b) Restwell Ltd, a hotel leisure company, is currently considering taking over a smaller private limited company, Staygood Ltd. The board of Restwell is in the process of making a bid for Staygood, but first needs to place a value on the company. Restwell has gathered the following data:
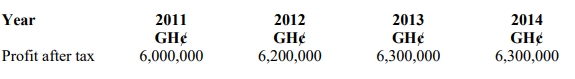
The company’s earnings yield is 12%.
Required:
i) As a Finance Manager, calculate the value of the company based on the present value of expected earnings.
(6 marks)
ii) Explain THREE problems associated with using the P/E method for valuing firms.
(3 marks)
Answer
a) The Three Basic Forms of the EMH
The efficient market hypothesis assumes that markets are efficient. However, the
efficient market hypothesis (EMH) can be categorized into three basic levels:
Weak-Form EMH
The weak-form EMH implies that the market is efficient, reflecting all market
information. This hypothesis assumes that the rates of return on the market
should be independent; past rates of return have no effect on future rates. In this
event that the stock market has weak-form efficiency, the price of Clear Tel will
move in line with historical changes.
Semi-Strong EMH
The semi-strong form EMH implies that the market is efficient, reflecting all
publicly available information. This hypothesis assumes that stocks adjust
quickly to absorb new information. The semi-strong form EMH also incorporates
the weak-form hypothesis. Given the assumption that stock prices reflect all new
available information and Clear Tel purchase stocks after this information is
released, Clear Tel cannot benefit over and above the market by trading on new
information.
Strong-Form EMH
The strong-form EMH implies that the market is efficient: it reflects all
information both public and private, building and incorporating the weak-form
EMH and the semi-strong form EMH. Given the assumption that stock prices
reflect all information (public as well as private) Clear Tel would not be able to
profit above the average investor even if he was given new information.
b) Restwell Ltd
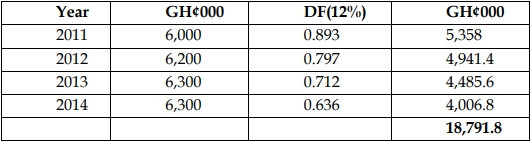
The value of the company based on the present value of expected earnings is
GH¢18,791,800.
ii) Problems associated with P/E method for valuing firms
- Doesn’t account for growth- The price to earnings ratio doesn’t account for any
type of growth or the lack of growth. The fact that growth isn’t factored in means
that older more mature stocks are typically going to appear cheaper even if they
aren’t growing if you use the P/E ratio. For many investors growth is a variable
they do not want to exclude. - Backward looking- The P/E ratio is actually a backward looking indicator if you
use the company’s most recent full year earnings number. A backward looking
number can be of very little help to the investor during a period where economic
conditions have changed significantly in a short period of time. - Quality of earnings not considered- The last several months have been the
perfect example of how a company can really inflate their earnings to look better
than they really are. Many banks were able to do this for months, and because of
that investors that solely used the P/E ratio would have thought they were great
buys. In retrospect if the investor had been looking at other parts of the balance
sheet they may have seen inflated earnings as a real issue. - The Price doesn’t consider debt- Companies with major debt issues are
obviously higher risk investments, but the P in the P/E ratio only considers the
equity price and does nothing with the debt that the business has to continue
with operations. As we have found out over time, excess debt can be a real
problem, and the market price of a stock isn’t always a good gauge of fair value. - Uses profit which is not cash
- Tags: Business Valuation, Earnings Yield, Efficient Market Hypothesis, P/E Ratio, Stock Market
- Level: Level 2
- Topic: Business valuations
- Series: MAY 2019
- Uploader: Joseph
