- 20 Marks
Question
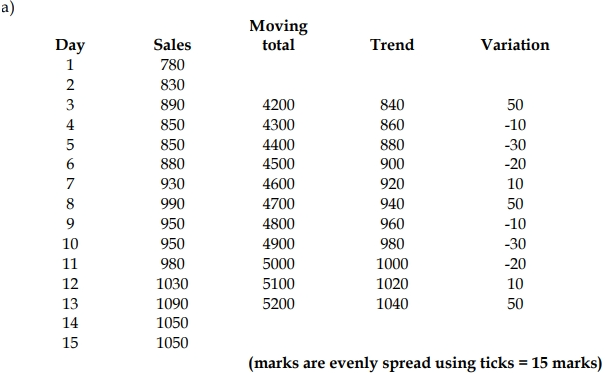
a) BB Importers Ltd has been importing electrical gadgets through the port of Takoradi over the past ten years. Management is aware that the business has been facing seasonal fluctuations but there is no scientific basis for the determination of such variations that can be used to predict future revenue. As a newly recruited Cost Accountant, you have been provided with some past daily sales performance over a three-week period. Details of the sales performance are shown below:
| Sales | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | 780 | 830 | 890 | 850 | 850 |
| Week 2 | 880 | 930 | 990 | 950 | 950 |
| Week 3 | 980 | 1030 | 1090 | 1050 | 1050 |
Required:
Using daily moving averages, calculate the daily variation for the company. (15 marks)
b) The reasons for variances might be connected, and two or more variances may arise from the same cause. For example, a favorable variance and an adverse variance might have the same cause.
Required:
Explain the interrelationships between:
i) Material price and usage variances (2.5 marks)
ii) Labor rate and efficiency variances (2.5 marks)
Answer
b) Interrelationship between variances
- Material price and usage variances: It may be decided to purchase cheaper
materials for a job in order to obtain a favourable price variance. This may lead to
higher materials wastage than expected and therefore, adverse usage variances
occur. If the cheaper materials are more difficult to handle, there might be some
adverse labour efficiency variance too. If a decision is made to purchase more
expensive materials, which perhaps have a longer service life, the price variance
will be adverse but the usage variance might be favourable. (2.5 marks) - Labour rate and efficiency variances: If employees in a workforce are paid higher
rates for experience and skill, using a highly skilled team should incur an adverse
rate variance at the same time as a favourable efficiency variance. In contrast, a
favourable rate variance might indicate a high proportion of inexperienced
workers in the workforce, which could result in an adverse labour efficiency
variance and possibly an adverse materials usage variance (due to high rates of
rejects). (2.5 marks)
- Tags: Material Price Variance, Moving Averages, Sales Forecasting, Usage Variance
- Level: Level 1
- Topic: Forecasting, Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
- Series: MAR 2024
- Uploader: Joseph
