- 20 Marks
Question
Question:
a) Balan Ltd is engaged in manufacturing and selling a single product and is in the process of preparing its budget for 2024. The following information is available:
Sales:
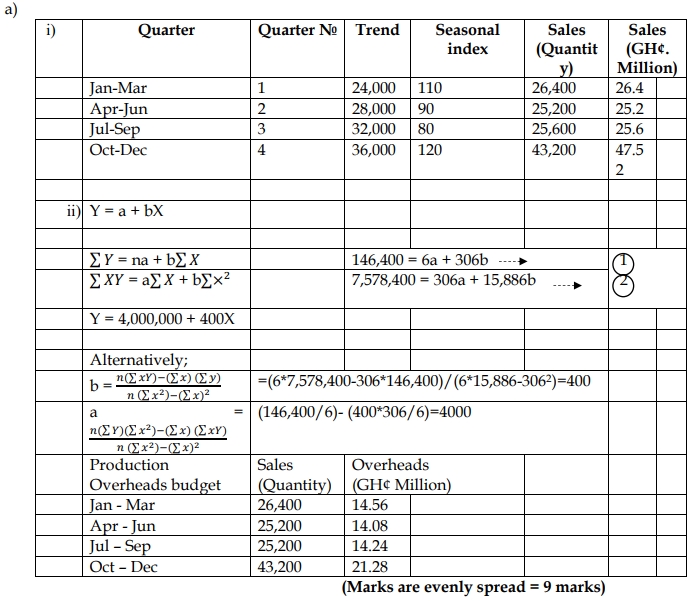
Balan Ltd has developed the linear relationship Y = 20,000 + 4,000X, where X represents the time period (X = 1 for the 1st quarter of 2024) and Y represents the sales trend in units.
The following seasonal variations are required to be adjusted to the sales trend in order to arrive at the sales forecast:
| Quarter | Jan-Mar | Apr-Jun | Jul-Sep | Oct-Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index value | 110 | 90 | 80 | 120 |
A unit of product can be sold at GH¢1,000 during the first three quarters, and this price will be increased by 10% in the fourth quarter of 2024.
Production Overheads:
Based on the past 6 quarters’ results, the following statistical data has been gathered:
n = 6 (where ‘n’ is the number of quarters considered)
∑X = 306 (where ‘X’ is the production quantity in thousands of units)
∑Y = 146,400 (where ‘Y’ is the total production overheads in GH¢ thousands)
∑XY = 7,578,400
∑X² = 15,886
Balan Ltd estimates a linear relationship between output (X) and production overheads (Y), and the total production overheads can be expressed as Y = a + bX.
Balan Ltd does not maintain finished goods inventories. You are one of the Management Accounting executives of Balan Ltd and have been requested to assist in compiling budget figures.
Required:
i) Prepare the seasonally adjusted quarterly sales forecast in unit and in value for the calendar year 2024. (4 marks)
ii) Prepare the quarterly production overheads budget for the calendar year 2024. (5 marks)
b) Explain the following terms:
i) Trend-Cycle (C) (2 marks)
ii) Seasonal Components (S) (2 marks)
iii) Irregular Components (I) (2 marks)
c) The purpose of Management Accounting is to provide information for planning, control, and decision making. Information for control of the performance is an important management task.
Required:
Outline THREE (3) activities involved in providing information for control purposes. (5 marks)
Answer
b.) Seasonal adjustment separates a time series into trend-cycle, seasonal, and
irregular components.
i) Trend-Cycle (C):
This component represents the long-term movement or pattern in a time series, which is typically derived from surrounding years or periods of observations. It shows the underlying direction in which the data is moving, whether upward, downward, or stagnant, over an extended period. (2 marks)
ii) Seasonal Components (S):
Seasonal components are regular, predictable fluctuations that occur within specific periods such as months or quarters. These effects are stable in timing, direction, and magnitude and can be caused by factors like weather patterns, holidays, or other recurring events. (2 marks)
iii) Irregular Components (I):
Irregular components are unpredictable fluctuations in a time series that cannot be attributed to trend or seasonal effects. They are usually short-term, random variations caused by unforeseen events such as natural disasters, strikes, or economic shocks. (2 marks)
c) Activities Involved in Providing Information for Control Purposes:
- Monitoring Actual Performance: This involves tracking and measuring actual outcomes against planned or budgeted objectives to assess performance.
- Evaluating Actual Performance: This step involves analyzing the data to determine how well the organization has met its goals and identifying areas of improvement.
- Taking Control Action: If there are deviations from the plan, corrective actions are taken to bring performance back in line with objectives. This may involve adjusting processes, reallocating resources, or revising targets.
(3 points @ 1.667 marks each = 5 marks)
- Topic: Budgeting, Forecasting
- Series: JULY 2023
- Uploader: Joseph
